The tech world is buzzing with news about Intel’s latest developments in the graphics domain. The company’s new Xe3P graphics technology is set to complement its promising Nova Lake CPU family. This advancement is significant for both desktop and mobile segments, as the Xe3P architecture is expected to bring a fresh wave of innovation to the industry.
Intel’s Next-Gen Graphics on the Horizon
Reports suggest that Intel is moving forward with the inclusion of its “Xe3P” graphics architecture, which was recently announced alongside Xe3. While the Xe3 is confirmed for the Panther Lake series, the latest Linux Kernel patches reveal that Xe3P will also be associated with Intel’s Nova Lake, the successor to Arrow Lake planned for release next year.
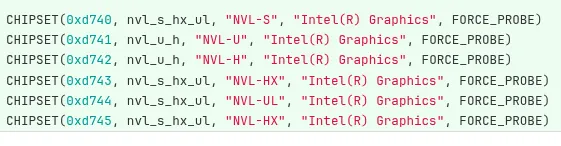
Sources have stated that Intel has just rolled out its initial Xe3P kernel graphics driver patches, anticipated to feature in the Linux 6.19 kernel cycle. These updates aim to extend open-source support for Intel’s next-gen GPU architecture, offering Linux users day-one support upon the Nova Lake’s arrival. Additionally, Mesa 26.0 has incorporated initial support for Xe3P, with patches highlighting several Nova Lake families like the S, U, H, HX, and UL variants within Mesa’s Iris Gallium3D (OpenGL) and ANV (Vulkan) drivers. This evidence indicates Intel’s preparation for extensive platform coverage of its upcoming CPUs and iGPU.
Challenges and Limitations of Xe3P Integration
Currently, the patches introduce new PCI Device IDs, laying the foundation rather than the complete feature set. This mirrors previous Xe3 implementations for Panther Lake and Wildcat Lake. The present support for Nova Lake Xe3P graphics remains experimental, requiring manual activation via a “force_probe” environment variable. This signals that the code isn’t yet ready for production, but stability is expected with future kernel release cycles.
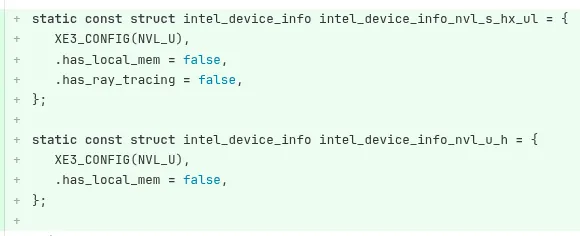
An essential aspect to highlight is the limited Ray-Tracing support across different Nova Lake variants. Not all chips in the Nova Lake lineup will feature Ray Tracing capabilities, as the Nova Lake-S, HX, and UL variants do not appear to possess the necessary hardware. Conversely, Nova Lake-U and Nova Lake-H variants seem equipped and ready for RT integration.
