Intel is making waves in the server industry with a strategic revamp aimed at enhancing memory bandwidth capabilities. The tech giant has decided to focus exclusively on developing its 16-channel Diamond Rapids processors, a move driven by the increasing demand for superior memory performance in data centers.
The Shift Toward 16-Channel Processors
Recent reports have highlighted a significant pivot in Intel’s server segment roadmap. With the release of the Diamond Rapids series scheduled for 2026, Intel has opted to eliminate the 8-channel variant from its lineup. This change stems from the need to cater to higher memory demands in the server market, which cannot be adequately met by the 8-channel processors that were to follow the Granite Rapids-SP lineup.
We have removed Diamond Rapids 8CH from our roadmap. We’re simplifying the Diamond Rapids platform with a focus on 16 Channel processors and extending its benefits down the stack to support a range of unique customers and their use cases.
– Intel to STH
Maximizing Bandwidth for Modern Needs
Intel’s decision to favor 16-channel processors is strategic, as they offer higher memory capacity and bandwidth, which are critical for modern server workloads such as AI and large-scale virtualization. Reports suggest that the 16-channel Diamond Rapids will support memory frequencies up to 12,800 MT/s, providing a staggering 1.6 TB/s of memory bandwidth. 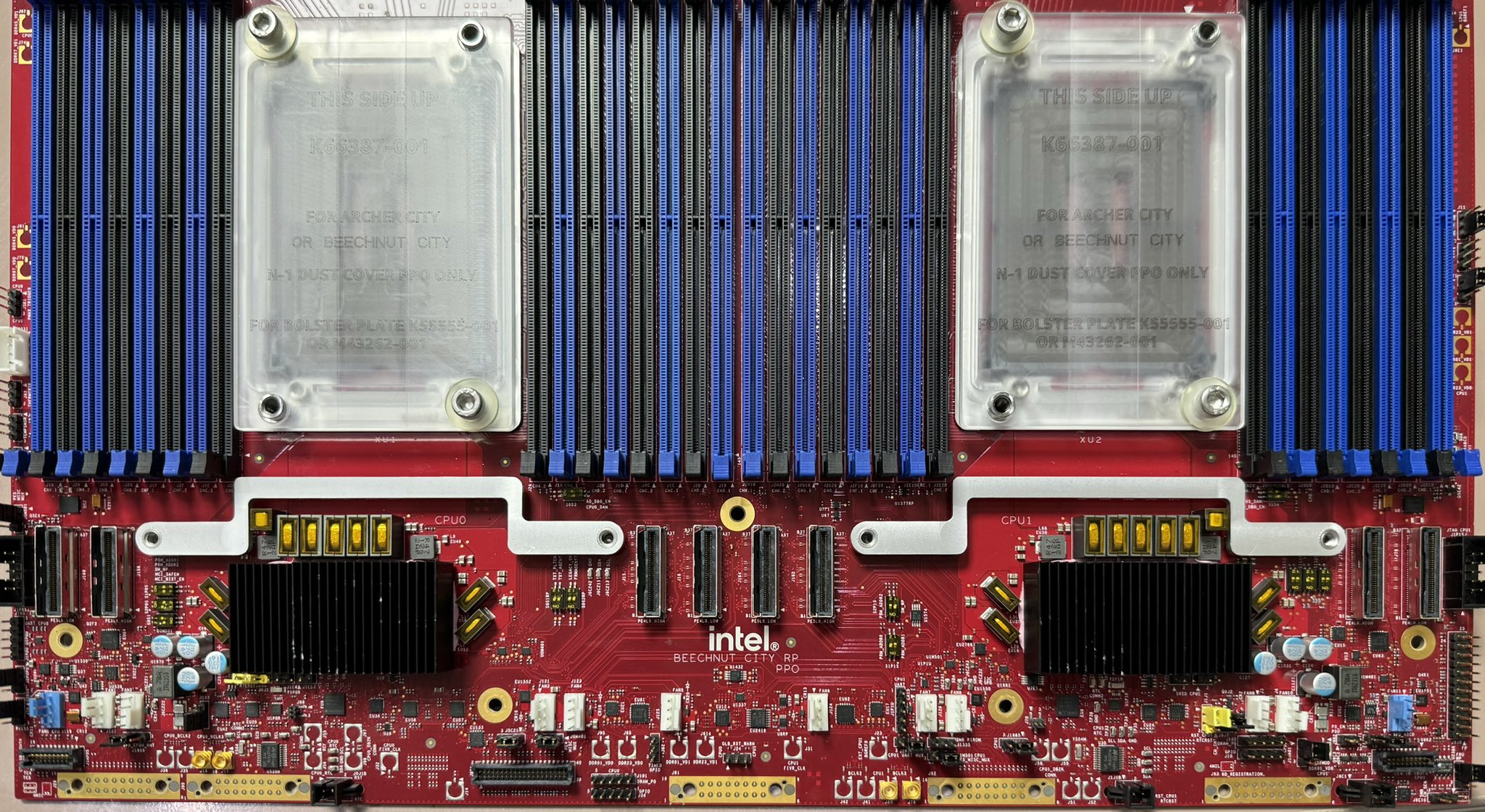
Competing in the Server Market
By adopting a 16-channel configuration, Intel aims to strengthen its position against AMD’s EPYC series, which is also gravitating towards higher memory-channel counts. Although the 8-channel design had cost advantages, its long-term viability is questionable amid evolving workload demands. Intel’s new focus on balancing cost and performance is a calculated move to remain competitive in the server CPU market.
