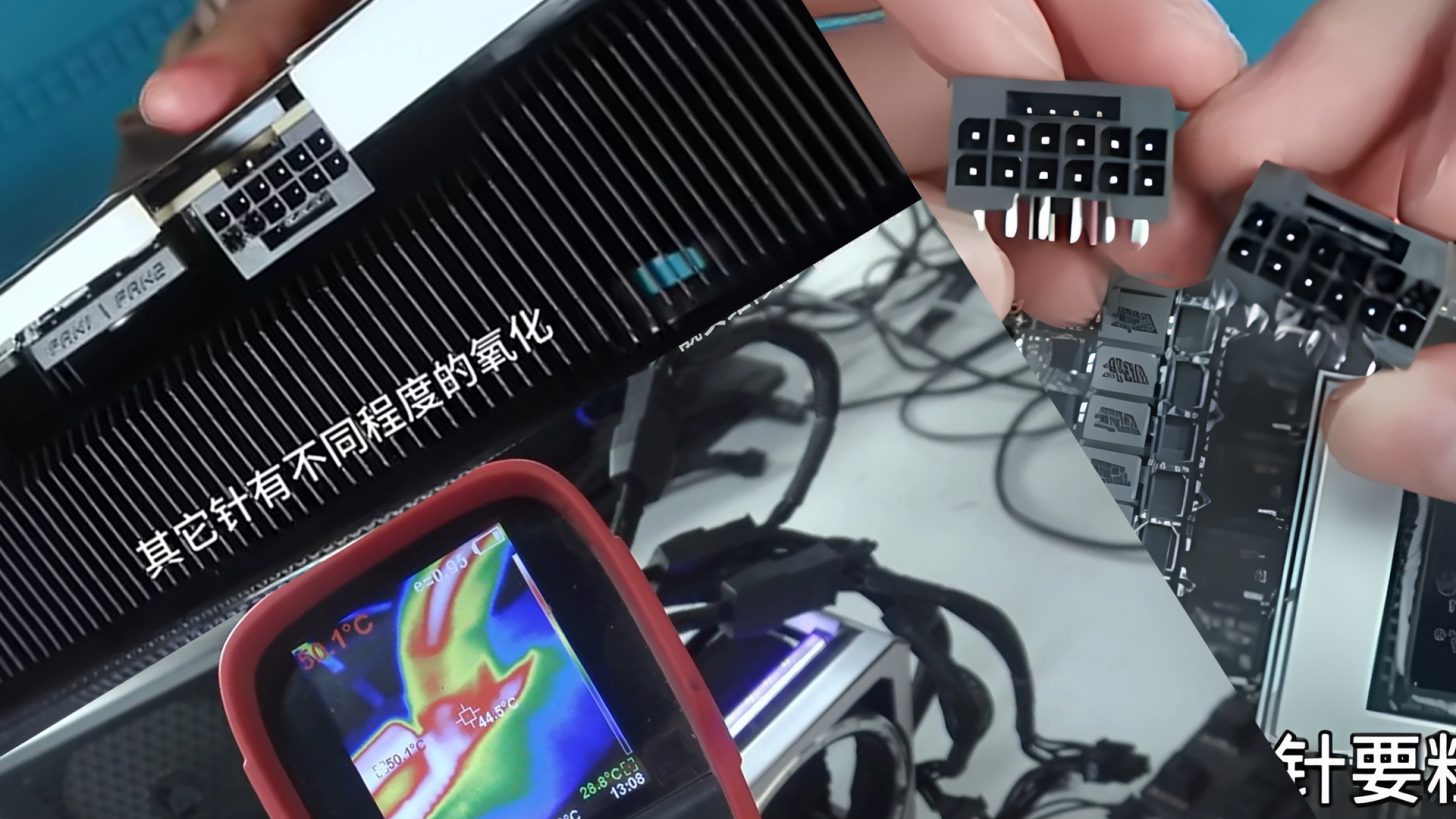
The gaming world is buzzing with a potential solution to a persistent issue affecting high-end RTX 50 series GPUs. A design flaw in the 16-pin connectors has led to numerous instances of melting, but recent developments suggest a promising fix. A female technician in China has demonstrated a practical approach to resolving this problem by using connectors with thicker pins.
Innovations in GPU Connector Design
The 16-pin connector has been a hot topic due to its high current density requirements, averaging 9.2A per pin and 55A in total. When some pins fail to make proper contact, the increased load can lead to excessive temperatures, resulting in melted connectors. Various fixes, such as color-coded connectors and adapters, have been tried but often fall short. The solution may lie in thicker pins, as shown by a repair specialist who successfully fixed a melted connector on an ROG Astral RTX 5090 GPU.
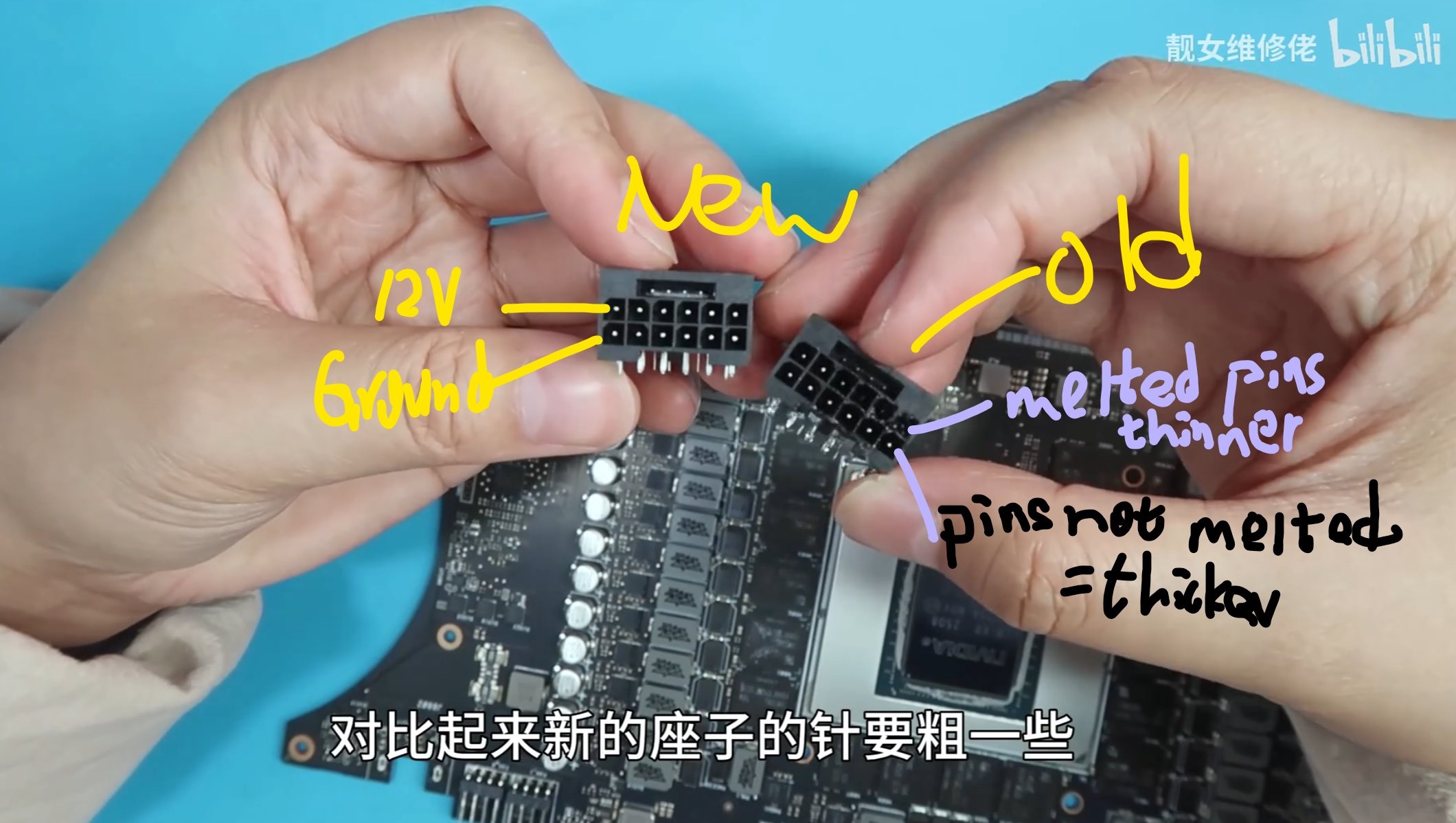
Thicker Pins: A Promising Solution
Replacing the melted 16-pin connector with one featuring thicker pins showed significant improvement. The technician observed the connector temperature at full load, which stabilized around 45°C at 600W. This is a marked improvement over previous temperatures that exceeded 100°C and, in extreme instances, approached 150°C. This indicates that thicker pins could be a viable solution to the melting problem, potentially leading to fewer failures and increased reliability. While the use of adapters remains discouraged, this new connector design seems to offer a promising path forward.

Ongoing efforts to address these connector issues are crucial, and while thicker pins might not be the ultimate solution, they certainly reduce the likelihood of failures. The added thickness provides better mechanical and electrical connectivity, leading to fewer “user error” incidents. As the RTX 50 series continues to utilize the 16-pin connector, the industry eagerly anticipates manufacturers adopting this improved design.
